Artificial Intelligence (AI) is paradigm-shifting and set to change everything. However, it’s important to be aware of the political, social, and ethical implications of this new technology as it develops. What are the political, social, and ethical implications of AI and how can we position ourselves to take advantage of the positive and protect ourselves from the negative implications of AI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative technology with significant political, social, and ethical implications. This essay/report explores the potential positive and negative impacts of AI and discusses strategies for leveraging its benefits while mitigating its risks.
Introduction
Background on Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly advancing and exerting a profound influence on various aspects of our daily lives. AI is fundamentally altering the way we work and interact, both in obvious and subtle ways. As AI becomes increasingly intertwined with our existence, it is crucial to take into account the ethical, political, and social consequences of this revolutionary technology.
The political repercussions of AI are extensive, impacting governance, policy-making, international relations, and diplomacy. The utilization of AI in government processes and decision-making has the potential to revolutionize the formulation and implementation of policies. This also raises concerns regarding data privacy, regulation, and legislative considerations.
At a societal level, AI has the potential to reshape the employment landscape and workforce dynamics. It has implications for education and skills development, as well as for social interactions and relationships. The impact of AI on inequality and the equitable distribution of its benefits within society also necessitates consideration.
From an ethical standpoint, there are significant apprehensions concerning privacy, data protection, as well as bias and discrimination in AI algorithms. The responsibility and accountability of AI systems are critical considerations that must be tackled to ensure the ethical deployment of AI.
To harness the positive potential of AI, there is a need to identify opportunities for innovation and growth while investing in the research and development of ethical AI solutions. Conversely, safeguarding against negative implications necessitates the development of robust ethical frameworks and the promotion of transparency in AI systems.
In conclusion, it is apparent that the impact of artificial intelligence extends beyond technological progress. Its ramifications extend to politics, society, and ethics, demanding careful deliberation as we continue to integrate this transformative technology into our lives. See references: (Ryan, 2023)[1], (Event examines the ethics, politics and future of AI, 2024)[2], (Larbey, 2020, pages 1-5)[3], (eur-lex.europa.eu legal-content EN TXT HTML ?uri=CELEX 52021PC0206, 2024)[4], (Tai, 2024)[9], (Stahl et al., 2022)[13], (DSouza, 2023, pages 1-5)[17], (FRANKE, 2021, pages 6-10)[19], (Matus et al., 2023)[22].
Purpose of the report
This report explores the implications of artificial intelligence (AI) on political, social, and ethical dimensions. It emphasizes the need to understand AI’s impact on governance, policy-making, international relations, and diplomacy. Regulation and legislation are crucial to ensure ethical implementation aligned with societal values.
AI has the potential to alter employment, workforce dynamics, education, and skills development. It can also influence social interactions and relationships, prompting a reassessment of human engagement with technology and each other.
Ethical considerations include privacy, data protection, bias, and discrimination in AI algorithms. Responsibility and accountability frameworks are essential for ensuring ethical boundaries are maintained.
To harness AI’s positive potential, there is a need to identify opportunities for innovation and growth, invest in research and development, and establish robust ethical frameworks and guidelines. Transparency and explainability in AI systems are also important.
As AI is integrated into society, it is crucial to recognize both its benefits and risks. Understanding the political, social, and ethical implications of AI can help harness its potential for positive transformation while mitigating any adverse effects. See references: (Ryan, 2023)[1], (FA – PUB – 6.indd, n.d., pages 1-5)[11].
Political Implications of AI
Impact on governance and policy-making
The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on political arenas is extensive and has a profound effect on governance and policy formulation. The European Union (EU) has adopted a proactive stance towards AI, striving to establish reliable AI that prioritizes the welfare of people. The EU’s Coordinated Plan on Artificial Intelligence aims to hasten investment in AI and harmonize policies to prevent division within Europe. Additionally, the EU has introduced the first-ever legal framework on AI, which addresses the dangers of AI and positions Europe as a global leader.
In the United States, there is a strong emphasis on leadership in AI policy and governance. The recent executive order marks a crucial initial step in US leadership in AI policy, with a focus on cultivating talent and making the US the preferred hub for AI innovation. The order also underscores responsible AI methods and processes, as well as commitments to privacy and ethical use of AI. This signals a dedication to creating new opportunities for businesses and civil society while ensuring accountable use of AI.
Moreover, international endeavors are underway to tackle global challenges linked to AI. Collaborations between the US, the UK, and other allies aim to counter malicious uses of AI that contradict democratic values. This involves researching ways to counteract nefarious use of AI and engaging with international partners to limit access or acquisition of advanced AI tools by adversarial nations.
In summary, the political implications of AI have spurred worldwide initiatives to develop regulations, ethical standards, and forge alliances for addressing global challenges associated with this technology. See references: (A European approach to artificial intelligence, 2024)[6], (Kavanagh, 2024)[10], (DSouza, 2023, pages 41-45)[17], (jcookson, 2023)[29].
Influence on international relations and diplomacy
The influence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on the arena of international relations and diplomacy is of paramount importance. AI is increasingly being utilized as a diplomatic tool, bringing new issues to the forefront of the international agenda, challenging geopolitical relationships, and serving as a practical tool for decision-making, drafting, translation, negotiation support, and trend analysis. Moreover, nations with advanced AI capabilities can exert greater military, economic, and societal influence. This has profound implications for global governance and policy-making, creating both new opportunities and concerns regarding the protection of human rights.
In addition, ethical considerations are pivotal in the development and use of AI in diplomatic contexts. Concerns have been raised about ethics, fairness, justice, transparency, and accountability in AI algorithms. The risk of discrimination and bias in decisions made by AI systems is a major concern that needs to be addressed. It is crucial to establish ethical frameworks and guidelines to ensure that AI systems are fair, accountable, transparent, explainable, and inclusive.
Furthermore, the EU’s vision for sustainable and trustworthy AI through initiatives such as the Coordinated Plan on Artificial Intelligence aims to expedite investment in AI while addressing global risks associated with AI. However, there is also a need for greater international engagement to promote human-centric artificial intelligence initiatives.
In summary, AI has wide-ranging implications for international relations and diplomacy. It is imperative for governments worldwide to take into account the impact of AI on geopolitics while giving priority to ethical considerations in the development and use of AI systems. See references: (A European approach to artificial intelligence, 2024)[6], (Kavanagh, 2024)[10], (AI DIPLOMACY: geo-politics, topics and tools in 2023 | Diplo, 2024)[15], (FRANKE, 2021, pages 16-20)[19].
Regulation and legislation considerations
The responsible development and deployment of AI technology relies on regulation and legislation. Countries and organizations worldwide are establishing frameworks for governing AI ethics. Examples include AI Singapore’s program to enhance AI capabilities and Singapore’s Advisory Council on the Ethical Use of AI and Data. China has unveiled the ‘Next Generation AI Development Plan’, while Japan has a three-step strategy for AI development leading up to 2030. The European Union issued a Declaration on AI Cooperation and launched an Initiative on AI focusing on technological capacity, socioeconomic effects, legal standards, and ethics guidelines. In the United States, there has been a shift in the approach to AI governance across different presidential administrations, emphasizing safety, transparency, fairness, non-discrimination, and public trust in AI applications.
Viable legislation and policies addressing the challenges associated with AI underscore the importance of setting minimum standards for corporate social responsibility reporting. Updating moral and legislative frameworks alongside technology development is crucial, along with promoting new forms of technology assessment focused on ethical risk evaluation.
The variety of approaches to ethics and governance across different countries highlights the necessity for international collaboration and clear guidelines at both national and international levels. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 91-95)[3], (A European approach to artificial intelligence, 2024)[6], (Kavanagh, 2024)[10], (Cohen et al., 2020)[21].
Social Implications of AI
Changes in employment landscape and workforce dynamics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technology into various industries has far-reaching implications for the job market and workforce dynamics. As AI continues to advance, it is vital to consider its potential impact on employment and the overall labor force. Traditional job structures will need to be redefined to accommodate automation and AI advancements. Workers will need to adapt and acquire new skill sets that are flexible and adaptable in a rapidly changing technological landscape. It is crucial to implement retraining programs early on, even at the high school level, to ensure widespread access to future job opportunities.
Furthermore, there is a strong call for global and regional multi-stakeholder bodies focused on ethical AI governance to ensure that AI benefits and empowers people equally. Policies must be established to bridge economic, technological, and social digital divides, and support a fair transition while respecting fundamental freedoms and rights. The impact of AI on the labor market and economy raises concerns about inequality, concentration of power, privacy violations, discrimination, biases perpetuated by algorithms, manipulation risks in financial systems, and psychological impacts related to human-robot relationships.
It is imperative for governments to take a central role in studying, monitoring, and regulating AI to mitigate these potential negative consequences. Research into sociotechnical feedback loops using systems engineering and complexity theory is also needed to understand how AI interacts with society.
In summary, addressing the changes in the employment landscape due to advances in AI requires proactive measures such as retraining programs, multi-stakeholder governance bodies focused on ethics and equality in AI deployment, and systematic research into sociotechnical feedback loops related to AI’s impacts on workforces. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 56-60)[3], (DSouza, 2023, pages 16-20)[17], (Soltas, 2022, pages 6-10)[25].
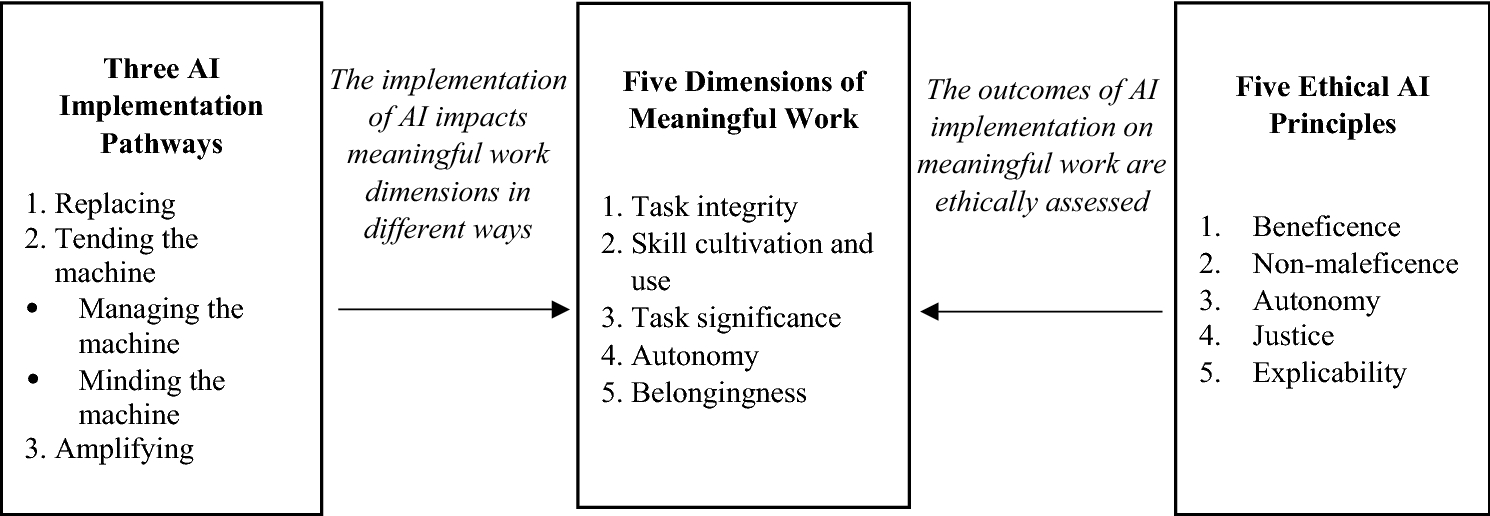
Figure 1: Overview of conceptual framework (source: reference (Bankins & Formosa, 2023)[32])
Impact on education and skills development
The influence of AI on education and skill development is multi-dimensional, with both advantageous and detrimental consequences. On the bright side, AI has the potential to transform the education system by customizing learning experiences, automating administrative tasks, and providing innovative teaching and learning tools. For instance, AI-driven tutoring systems can adjust to individual students’ learning styles and speed, helping to bridge educational gaps. Moreover, AI can aid in grading papers and delivering feedback, freeing up teachers’ time for more personalized interaction with students.
Conversely, the widespread use of AI in education raises ethical concerns regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and discrimination. There is a concern that AI systems could perpetuate existing systemic biases and unfairness for students from marginalized groups. Additionally, the use of AI in educational settings also brings up issues related to digital literacy and cybersecurity that need attention.
To address these challenges in K-12 settings, there is a critical need to educate teachers and students about the ethical challenges posed by AI applications. This includes creating opportunities for K-12 students and teachers to learn about AI through ethics-based curricula and professional development. Open-access resources such as “AI and Ethics” curriculum from MIT Media Lab and “AI and Data Privacy” workshop offer instructional materials for educators aiming at addressing these ethical challenges.
In conclusion, while AI presents significant opportunities for innovation in education, it also raises important ethical concerns that need attention. By investing in resources for teaching about AI ethics at an early age and developing robust ethical frameworks for its use in educational settings, we can work towards ensuring that the impact of AI on education is positive rather than detrimental. See reference (Akgun & Greenhow, 2022)[5].

Figure 2: Research about AI is growing rapidly. Other indicators, such as dollars invested and number of people employed, show similar trends. (source: reference (Education, 2023)[33])
Effects on social interactions and relationships
The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on social interactions and relationships is far-reaching and multifaceted. One of the primary effects is the potential disruption of the labor market and workforce dynamics. AI systems are increasingly automating tasks, leading to changes in job roles and employment opportunities, which can significantly affect the dynamics of social interactions within work environments.
Moreover, the integration of AI technology has implications for education and skills development. As AI advances, there is a growing demand for individuals to acquire new skills and knowledge to remain competitive in the workforce. This can create a divide between those with access to AI-related education and training and those without, potentially widening existing social inequalities and impacting social interactions.
Additionally, AI has the potential to reshape social relationships by influencing how people interact with technology. The widespread use of AI-driven applications in fields like e-commerce and finance can alter human behaviors and communication patterns. Furthermore, ethical concerns related to AI, such as privacy issues and algorithmic biases, can impact trust within social interactions.
In conclusion, the emergence of AI brings about significant changes in social interactions and relationships, including shifts in employment dynamics, impacts on education and skills development, as well as alterations in human-technology interactions. It is crucial for policymakers, organizations, and individuals to address these implications to ensure that AI contributes positively to society while minimizing potential negative effects. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 91-95)[3], (Manirambona, 2020, pages 11-15)[14], (Center, 2022)[26].
Ethical Implications of AI
Privacy and data protection concerns
The ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI) revolve around privacy and data protection. The collection and use of personal data by AI systems raise significant privacy concerns, necessitating a balance between data utilization and privacy rights. Comprehensive regulations are crucial to oversee the handling of personal data by AI systems, especially as AI becomes more integrated into society.
Bias and discrimination in AI algorithms can worsen privacy concerns and lead to discriminatory outcomes that disproportionately affect certain groups. Responsible use of AI in social media marketing requires ethical and transparent AI solutions that prioritize individual trust and minimize privacy invasion.
To address these concerns, it is important to invest in ethical AI solutions that prioritize user privacy and adhere to data protection principles. Promoting transparency in AI systems is essential for individuals to understand how their data is being used.
In conclusion, addressing privacy and data protection concerns within AI requires a comprehensive approach that includes regulatory measures, ethical considerations, and technological advancements. Prioritizing individual privacy rights and implementing responsible AI practices can help mitigate potential harms while harnessing the benefits of artificial intelligence. See references: (Ryan, 2023)[1], (Larbey, 2020, pages 51-55)[3], (Commission, 2020, pages 11-15)[7], (Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions, 2021)[8], (Stahl & Leach, 2023)[20].
| Ethical Principles | No. of times found in the 21 papers analysed for this paper | No. of times found in the 84 AI ethics guidelines analysed by Jobin et al. 2019 |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | 595 | 14 |
| Non-maleficence | 228 | 60 |
| Trust | 209 | 28 |
| Beneficence | 122 | 41 |
| Freedom and Autonomy | 68 | 34 |
| Privacy | 66 | 47 |
| Justice and Fairness | 53 | 68 |
| Responsibility | 47 | 60 |
| Transparency | 19 | 73 |
| Solidarity | 2 | 6 |
| Dignity | 1 | 13 |
Table 1: The 11 overarching principles identified in our research (left) beside the number of times those searches appeared in the 84 AI ethics guidelines that Jobin et al. 2019 analysed (right) (source: reference (Ryan, 2023)[1])

Figure 3: General principles for the ethical and values-based design, development, and implementation of autonomous and intelligent systems (as defined by the IEEE’s Ethically Aligned Design First Edition March 2019) (source: reference (Larbey, 2020)[3])
Bias and discrimination in AI algorithms
The ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI) are a major concern, particularly in terms of privacy and data protection. As AI technology advances, the collection and use of personal data raise significant privacy issues. It is crucial to find a balance between innovation and respect for individuals’ privacy rights. Regulations overseeing the gathering, storage, and utilization of personal data by AI systems are necessary, especially as AI becomes more integrated into various aspects of society.
Bias and discrimination in AI algorithms can exacerbate privacy concerns and have ethical implications. Without fairness and inclusivity in mind, there is a heightened risk of discriminatory outcomes that could disproportionately affect certain groups. Responsible AI-driven social media marketing is another area of concern, requiring ethical and transparent AI solutions that prioritize individual trust and minimize privacy invasion.
To address these concerns, it is essential to invest in research and development of ethical AI solutions that prioritize user privacy and adhere to established data protection principles. This includes promoting transparency in AI systems to ensure individuals understand how their data is being used.
In conclusion, addressing privacy and data protection concerns in AI requires a comprehensive approach that combines regulatory measures, ethical considerations, and technological advancements. By prioritizing individual privacy rights and implementing responsible AI practices, it is possible to mitigate potential harms while harnessing the benefits of artificial intelligence. See references: (Akgun & Greenhow, 2022)[5], (Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy, 2023)[12], (AI DIPLOMACY: geo-politics, topics and tools in 2023 | Diplo, 2024)[15], (Stahl & Leach, 2023)[20], (Soltas, 2022, pages 6-10)[25], (ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope, 2023)[28], (House, 2023)[31].
Responsibility and accountability of AI systems
When it comes to the development and implementation of AI systems, responsibility and accountability are essential. As AI becomes more ingrained in our daily lives, it is crucial to ensure that the technology is used ethically, while maintaining democratic politics and informed and humane policies. Trustworthy AI must be lawful, ethical, and robust from both a technical and social perspective, complying with all applicable laws and regulations, adhering to ethical principles and values, and ensuring collaboration among technologists, policymakers, ethicists, and society at large. It is our individual and collective responsibility as a society to strive towards ensuring that all three components – legality, ethics, and robustness – contribute to securing Trustworthy AI.
The use of AI-powered autonomous weapons raises ethical concerns regarding accountability, potential misuse, and loss of human control over life-and-death decisions. This underscores the need for international agreements and regulations to govern their use in order to prevent catastrophic consequences.
Ethical considerations in AI bioethics are crucial in preventing unintended harm caused by AI. In light of experts’ warnings about the potential threat of full AI development to humankind, implementing principles for using AI with transparency, accountability, explainability, and interpretability becomes essential for guiding the future development of AI technology.
Several initiatives acknowledge that accountability is vital for holding developers responsible for harm caused by AI systems. There is also a need for new standards detailing measurable levels of transparency so that systems can be objectively assessed for compliance with initiatives focusing on societal harms of AI.
In conclusion, promoting responsible deployment through collaboration among various stakeholders is integral in ensuring the responsible development and use of AI systems while upholding ethical principles. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 1-5)[3], (Commission, 2020, pages 6-10)[7], (Tai, 2024)[9], (www.nuffieldfoundation.org sites default files files Ethical-and-Societal-Implications-of-Data-and-AI-report-Nuffield-Foundat.pdf, 2019, pages 46-50)[24], (The Ethical Considerations of Artificial Intelligence | Capitol Technology University, 2024)[27].
Positioning for Positive Implications of AI
Identifying opportunities for innovation and growth
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) presents vast opportunities for addressing global climate change, but it’s essential to consider the environmental impact of AI research. The USA, China, and India are focusing on the economic and societal benefits of AI, with a focus on inclusive growth and technological leadership. There are also opportunities for using AI to address social challenges and benefit humanity through ethical AI principles. To seize these opportunities, it’s crucial to invest in research and development of ethical AI solutions, promote responsible governance, and engage with stakeholders to ensure that AI technologies benefit and empower as many people as possible. Ultimately, aligning policies with these opportunities and fostering cross-disciplinary research efforts can lead to a more sustainable society that leverages the full potential of ethical artificial intelligence. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 81-85)[3], (Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy, 2023)[12], (Tsamados et al., 2023)[18].
Investing in research and development of ethical AI solutions
Investing in research and development of ethical AI solutions is crucial for reaping the benefits of AI while minimizing potential risks. The “AI for social good” report emphasizes the need to explore generative AI for socially beneficial purposes through interdisciplinary research and educational programs. The impact of AI on governance, policy-making, and international relations underscores the significance of developing appropriate policies and regulations for AI. The European Union and countries like Malta, Poland, Russia, and the United States have prioritized the development of ethical AI policies, reflecting global acknowledgment of the necessity to invest in ethical AI.
Addressing ethical concerns such as algorithmic fairness, biases, data privacy, safety, transparency, and intellectual property law is crucial. Establishing a system based on public trust through robust ethical principles will ensure that everyone benefits from AI. National strategies and independent ethical initiatives for AI are increasing globally, with countries like Germany, the UK, India, Singapore, Mexico, and the UAE committing to establishing AI ethics councils. Investing in ethical AI solutions is essential for promoting responsible competitiveness and positioning Europe as a global leader in trustworthy AI systems. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 91-95)[3], (Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy, 2023)[12], (Manirambona, 2020, pages 11-15)[14], (Soltas, 2022, pages 41-45)[25].
Protecting Against Negative Implications of AI
Developing robust ethical frameworks and guidelines
Creating strong ethical frameworks and guidelines is essential for ensuring the responsible use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and upholding ethical values. Trustworthy AI should be both lawful and ethical, with all components working together to promote responsible competitiveness. It is our shared responsibility as a society to ensure that AI systems are reliable and adhere to ethical standards, fostering responsible and sustainable AI innovation. These frameworks should address privacy concerns, bias, discrimination in AI algorithms, and the responsibility and accountability of AI systems, minimizing unintended harm.
Investing in research and development of ethical AI solutions is crucial for identifying opportunities for innovation and growth, with a focus on creating AI systems that benefit society while upholding ethical principles. Establishing strong ethical frameworks guiding the design, development, and utilization of AI can enhance transparency and explainability in AI systems and help mitigate potential risks associated with autonomous decision-making processes driven by AI. Overall, integrating ethics into the core development of AI systems is crucial for ensuring that AI operates within legal boundaries while upholding ethical principles, positioning us as global leaders in cutting-edge AI deserving of trust. See references: (Larbey, 2020, pages 81-85)[3], (Commission, 2020, pages 6-10)[7], (Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy, 2023)[12], (Ethics of Artificial Intelligence | Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, 2024)[16], (The Ethical Considerations of Artificial Intelligence | Capitol Technology University, 2024)[27].
Promoting transparency and explainability in AI systems
Encouraging openness and clarity in AI systems is crucial for responsible development and usage, especially as AI becomes more integrated into daily life. Transparency and accountability are essential to prevent the exploitation of AI-generated content and establish guidelines for its responsible use. Responsible AI should be a part of strategic implementation and business planning, focusing on ethical and accountable solutions.
Incorporating responsible AI into social media marketing includes developing ethics policies and considering socially beneficial AI approaches. Understanding how to best support AI development, deployment, and usage is crucial for building a better future while remaining globally competitive. This involves addressing ethical challenges related to the impact of AI on individuals and society, decision-making capabilities, safety concerns, fairness, inclusion, and employment equality.
To achieve these objectives, it is important to foster a culture of collaboration, trust, and transparency and implement guidelines from various organizations such as governmental agencies and professional associations. Promoting transparency and explainability in AI systems requires a collective effort from all stakeholders, including developers, businesses, policymakers, researchers, and ethicists. The incorporation of responsible AI into strategic implementation processes and the establishment of ethics policies will help ensure that AI development and deployment align with societal values while minimizing potential negative impacts. See references: (Commission, 2020, pages 11-15)[7], (Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions, 2021)[8], (www.nuffieldfoundation.org sites default files files Ethical-and-Societal-Implications-of-Data-and-AI-report-Nuffield-Foundat.pdf, 2019, pages 46-50)[24], (ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope, 2023)[28].
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ethical, social, and political implications of artificial intelligence (AI) are extensive and multifaceted. The widespread use of AI across various industries has the potential to greatly influence governance, policy-making, international relations, employment dynamics, education, social interactions, privacy, and data protection. It also raises concerns about bias and discrimination in AI algorithms and the responsibility and accountability of AI systems.
Moving forward with AI technology demands identifying opportunities for innovation and growth while investing in research and development of ethical AI solutions. This encompasses creating robust ethical frameworks and guidelines, advocating for transparency and explainability in AI systems, and promoting collaboration between public and private sector organizations to ensure responsible use of these technologies.
Addressing the challenges posed by AI is essential to ensure that it benefits everyone. We must reconsider current regulatory frameworks to align with new technological developments. Public discourse on the ethics of AI-driven healthcare is crucial to address implications on the human workforce and society as a whole. By doing so, we can unleash the potential of AI while addressing the ethical and legal challenges ahead.
The insights from various studies contribute to a deeper understanding of the role of AI in organizations and its impact on modern societies. Ethical concerns related to AI involve fundamental trade-offs that necessitate informed political, legal, and professional discussions.
In conclusion, navigating the implications of artificial intelligence requires a multidisciplinary approach that takes into account not only technological advancements but also societal values, ethics, and human rights. See references: (Ryan, 2023)[1], (FA – PUB – 6.indd, n.d., pages 1-5)[11], (Stahl et al., 2022)[13], (Cohen et al., 2020)[21], (How artificial intelligence is transforming the world | Brookings, 2023)[23].
Recommendations
The responsible advancement and implementation of AI technologies require increased data accessibility while safeguarding personal privacy, additional funding for unclassified AI research, and new models of digital education and AI workforce development. It is also important to establish federal AI advisory committees, regulate broad AI principles, uphold human oversight, and control over AI systems, and penalize malicious AI behavior while promoting cybersecurity measures. These recommendations will help harness the opportunities presented by AI while mitigating potential risks. See references: (Event examines the ethics, politics and future of AI, 2024)[2], (Tsamados et al., 2023)[18], (FRANKE, 2021, pages 26-30)[19], (How artificial intelligence is transforming the world | Brookings, 2023)[23].
Appendix (Optional)
Detailed case studies/examples
The development of six fictional research proposals by the Ada Lovelace Institute, the University of Exeter’s Institute for Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, and the Alan Turing Institute stands out as a notable case study in the realm of AI and data science. These proposals were crafted to mimic potential submissions to a Research Ethics Committee, with the intention of sparking contemplation on prevalent research ethics issues and the societal repercussions of various AI and data science research projects. The expert workshop determined that case studies like these are valuable educational tools for grappling with ethical dilemmas in AI and data science.
Such case studies serve as an invaluable resource for students, researchers, members of research ethics committees, funders, and other key stakeholders within the research community. By engaging with these hypothetical scenarios, individuals can enhance their capacity to recognize and assess common ethical concerns within AI and data science research. This highlights the significance of ethical considerations in advancing AI technologies and emphasizes the necessity of sturdy ethical frameworks and guidelines to steer responsible AI development.
In addition to these fabricated research proposals, there exists a multitude of real-world instances that demonstrate both positive and negative impacts of AI. These instances encompass cases of bias and discrimination in AI algorithms, privacy issues linked to data protection, as well as prospects for innovation and progress through ethical AI solutions. By scrutinizing these case studies, stakeholders can attain a deeper comprehension of how AI is shaping our society politically, socially, and ethically. See reference (Looking before we leap, 2022)[30].
Additional resources for further reading
For those interested in delving deeper into the political, social, and ethical ramifications of Artificial Intelligence, there are a number of essential resources that offer valuable perspectives and suggestions. The national AI strategies released by EU Member States provide a comprehensive overview of the impact of AI on governance, policy-making, international relations, diplomacy, as well as regulatory and legislative considerations. These strategies also underscore the significance of ethical AI, with the EU playing a prominent role in defining it as a primary area of focus and effort.
In addition to the national strategies, there are proposals for international and European collaboration in AI research. Smaller states acknowledge the necessity of cooperating on groundbreaking fundamental AI research, while larger states like Germany and France have committed to establishing joint virtual research and development centers. The emphasis on promoting the use of AI for private firms is also evident in these strategies, with initiatives aimed at providing assistance for small and medium-sized companies to incorporate AI into their operations.
Moreover, these national strategies address the societal implications of AI, particularly its effects on employment opportunities and workforce dynamics. Countries such as Germany are implementing programs to enhance AI-specific support for businesses, including offering “AI trainers” to help companies integrate AI into their operations. There is also a focus on advancing education and skills development within the realm of AI, with initiatives aimed at creating platforms for business leaders to exchange experiences with AI.
Lastly, ethical considerations such as privacy and data protection concerns, bias and discrimination in AI algorithms, as well as the responsibility and accountability of AI systems are tackled across all national AI strategies. The EU has taken a leading role in promoting “trustworthy” AI as a primary area of focus and effort. See reference (FRANKE, 2021, pages 26-30)[19].
References
- [1] Ryan. Mark. (2023). The social and ethical impacts of artificial intelligence in agriculture: mapping the agricultural AI literature. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00146-021-01377-9
- [2] Event examines the ethics, politics and future of AI. (2024). https://government.cornell.edu/news/event-examines-ethics-politics-and-future-ai
- [3] Ruth Larbey. (2020). [‘The ethics of artificial intelligence: Issues and initiativ…he Future of Science and Technology AUTHORS This study has ‘]. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2020/634452/EPRS_STU(2020)634452_EN.pdf
- [4] eur-lex.europa.eu legal-content EN TXT HTML ?uri=CELEX 52021PC0206. (2024). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:52021PC0206
- [5] Selin Akgun, Christine Greenhow. (2022). Artificial intelligence in education: Addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8455229/
- [6] A European approach to artificial intelligence. (2024). https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/european-approach-artificial-intelligence
- [7] Independent High-Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence set up by the European Commission. (2020). Ethics Guidelines for AI. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/cmsdata/196377/AI%20HLEG_Ethics%20Guidelines%20for%20Trustworthy%20AI.pdf
- [8] Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. (2021). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401220308082
- [9] Michael Cheng-Tek Tai. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence on human society and bioethics. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7605294/
- [10] Camino Kavanagh. (2024). New Tech, New Threats, and New Governance Challenges: An Opportunity to Craft Smarter Responses?. https://carnegieendowment.org/2019/08/28/new-tech-new-threats-and-new-governance-challenges-opportunity-to-craft-smarter-responses-pub-79736
- [11] FA – PUB – 6.indd. (n.d.). https://wellcome.org/sites/default/files/ai-in-health-ethical-social-political-challenges.pdf
- [12] Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy. (2023). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401223000233
- [13] Stahl. Bernd Carsten, Ryan. Mark, Antoniou. Josephina, Jiya. Tilimbe, Macnish. Kevin. (2022). Organisational responses to the ethical issues of artificial intelligence. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00146-021-01148-6
- [14] Rachel Manirambona. (2020). [‘The impact of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)…ties between AI and data protection principles, such as, in’]. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2020/641530/EPRS_STU(2020)641530_EN.pdf
- [15] AI DIPLOMACY: geo-politics, topics and tools in 2023 | Diplo. (2024). https://www.diplomacy.edu/topics/ai-and-diplomacy/
- [16] Ethics of Artificial Intelligence | Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. (2024). https://iep.utm.edu/ethics-of-artificial-intelligence/
- [17] DSouza. Faisal CTR. (2023). [‘N ATIONAL A RTIFICIAL I NTELLIGENCE R ESEARCH AND D EVELOPM…logical analysis and judgment for the President with respec’]. https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/National-Artificial-Intelligence-Research-and-Development-Strategic-Plan-2023-Update.pdf
- [18] Andreas Tsamados, Mariarosaria Taddeo, Luciano Floridi, Josh Cowls. (2023). The AI gambit: leveraging artificial intelligence to combat climate change-opportunities, challenges, and recommendations. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8522259/
- [19] Ulrike FRANKE. (2021). Artificial Intelligence diplomacy | Artificial Intelligence governance as a new external policy tool. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2021/662926/IPOL_STU(2021)662926_EN.pdf
- [20] Stahl. Bernd Carsten, Leach. Tonii. (2023). Assessing the ethical and social concerns of artificial intelligence in neuroinformatics research: an empirical test of the European Union Assessment List for Trustworthy AI (ALTAI). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43681-022-00201-4
- [21] Glenn Cohen, Sara Gerke, Timo Minssen. (2020). Ethical and legal challenges of artificial intelligence-driven healthcare. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7332220/
- [22] Kira Matus, Robert Gorwa, Michael Veale. (2023). AI and Global Governance: Modalities, Rationales, Tensions. https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-lawsocsci-020223-040749
- [23] How artificial intelligence is transforming the world | Brookings. (2023). https://www.brookings.edu/articles/how-artificial-intelligence-is-transforming-the-world/
- [24] www.nuffieldfoundation.org sites default files files Ethical-and-Societal-Implications-of-Data-and-AI-report-Nuffield-Foundat.pdf. (2019). https://www.nuffieldfoundation.org/sites/default/files/files/Ethical-and-Societal-Implications-of-Data-and-AI-report-Nuffield-Foundat.pdf
- [25] Soltas. Evan J. EOP/CEA. (2022). [‘THE IMPACT OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ON THE FUTURE OF WORK… Will Be the Impact of AI on the Workplace?.22 Part IV: Cas’]. https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/TTC-EC-CEA-AI-Report-12052022-1.pdf
- [26] Pew Research Center. (2022). 2. Solutions to address AI’s anticipated negative impacts. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2018/12/10/solutions-to-address-ais-anticipated-negative-impacts/
- [27] The Ethical Considerations of Artificial Intelligence | Capitol Technology University. (2024). https://www.captechu.edu/blog/ethical-considerations-of-artificial-intelligence
- [28] ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. (2023). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266734522300024X
- [29] jcookson. (2023). Experts react: What does Biden’s new executive order mean for the future of AI?. https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/experts-react/experts-react-what-does-bidens-new-executive-order-mean-for-the-future-of-ai/
- [30] Looking before we leap. (2022). https://www.adalovelaceinstitute.org/report/looking-before-we-leap/
- [31] The White House. (2023). Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence | The White House. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
- [32] Bankins. Sarah, Formosa. Paul. (2023). The Ethical Implications of Artificial Intelligence (AI) For Meaningful Work. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10551-023-05339-7
- [33] U.S. Department of Education. (2023). Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning (PDF). https://www2.ed.gov/documents/ai-report/ai-report.pdf

Leave a Reply